Animagus 的设计者正是 CKB-VM 的设计者与核心开发者 Xuejie。在第一篇文章中,Xuejie 向我们介绍了 Animagus。本文是该系列的第二篇,将详细介绍如何运行 Animagus。
作者:Xuejie
原文链接:What’s Animagus Part 2: Running it For Real | by Nervos Network | Nervos Network | Medium
我们将实现 balance checker(余额检查器)AST,然后用 Animagus 启动它,这样就可以通过调用 RPC 请求来和 Animagus 进行交互了。
在正式开始之前,你的系统上需要有这几个依赖项:
-
Docker :虽然 Docker 不是在生产环境中运行 Animagus 的严格依赖项,但之后你将看到它可以帮助我们快速配置开发环境。
-
Go :Animagus 用 Go 语言编写。因为我们是从源代码构建 Animagus,所以需要在计算机上安装 Go。
-
Ruby: 我们使用 Ruby 构建 balance checker AST。虽然你可以使用 GRPC 支持的任何语言,但 Ruby 拥有非常好的 REPL ,可以用来更好地测试。
-
GRPC: 我们需要 Go 和 Ruby 的 GRPC 开发依赖项,可以参阅 GRPC 文档中的「快速入门」部分,并查找 Go 和 Ruby 的操作步骤。
在尝试开始下面步骤之前,请确保已安装上述组件并准备就绪。
注意:在 Unix 环境(例如 Linux,macOS 或 Windows 上的模拟解决方案)下尝试这些步骤会更好。如果在其他平台上进行测试,性能可能会有所不同。
首先,我们来编译 Animagus:
$ export TOP=$(pwd)
$ git clone https://github.com/xxuejie/animagus
$ cd animagus (https://github.com/xxuejie/animagus)
$ git checkout afb9f1ec5ca14493835c8aeb4651b5121580ce39
$ go build ./cmd/animagus
在生产环境中,Animagus 需要以下依赖项:
- CKB
- GraphQL server(为 CKB 提供的插件)
- Redis
为了简化大家的测试流程,我准备了一个 docker 镜像,它将 CKB 与 CKB GraphQL server 打包在一起,只需一个命令,就可以启动已经准备就绪的 CKB 实例。这里的结果是,依次输入以下命令,我们可以通过两个 docker 容器启动所需的所有的依赖项:
$ cd $TOP
$ mkdir ckb-data
$ docker run -d --rm -p 9115:9115 -v `pwd`/ckb-data:/data --env RPC_RATE=200000 --env GRAPHQL_RATE=200000 --name ckb xxuejie/perkins-tent
$ docker run -d --rm -p 6379:6379 --name redis redis:alpine
注意:为 CKB 提供的打包好的 docker 镜像是限制的。这里,我们对一些值做了修改,是为了减少测试过程中的等待时间,但如果要使用 docker 镜像运行公共节点,请确保将修改过的的值调整回去,以免造成 container 被滥用。
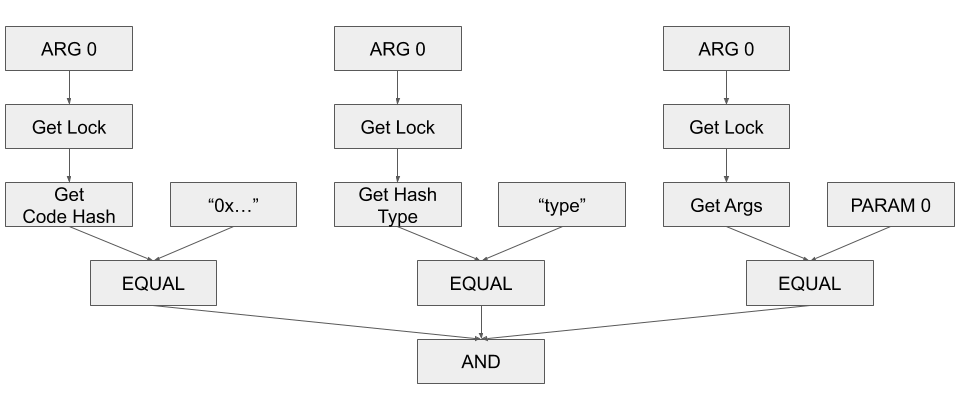
在等待 CKB 同步时,我们来启动 Ruby,并实现 balance checker AST。首先,我们要 在 balance checker AST 中构建查询部分 。请注意,完整的查询节点就是下面显示的附加到 QueryCell 节点的查询函数。
$ cd $TOP
$ cat << EOF > animagus/ruby/query_cell.rb
require_relative "ast_pb"
def build_query_cell_function
cell = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::ARG,
u: 0
)
script = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::GET_LOCK,
children: [cell]
)
expected_code_hash = [
"9bd7e06f3ecf4be0f2fcd2188b23f1b9fcc88e5d4b65a8637b17723bbda3cce8"
].pack("H*")
code_hash_value = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::BYTES,
raw: expected_code_hash
)
code_hash = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::GET_CODE_HASH,
children: [script]
)
code_hash_test = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::EQUAL,
children: [
code_hash,
code_hash_value
]
)
hash_type_value = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::UINT64,
u: 1
)
hash_type = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::GET_HASH_TYPE,
children: [script]
)
hash_type_test = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::EQUAL,
children: [
hash_type,
hash_type_value
]
)
args_value = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::PARAM,
u: 0
)
args = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::GET_ARGS,
children: [script]
)
args_test = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::EQUAL,
children: [
args,
args_value
]
)
Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::AND,
children: [
code_hash_test,
hash_type_test,
args_test
]
)
end
def build_query_cell
Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::QUERY_CELLS,
children: [
build_query_cell_function
]
)
end
EOF
这里的代码很长,但有大量的代码都是重复的,这是因为代码直接是在 AST 上实现的。有了 DRY 原理定义的一些函数,我们就应该能够构建出最小的 DSL,和 Animagus AST 一起使用。
下面就是转换的实现部分:
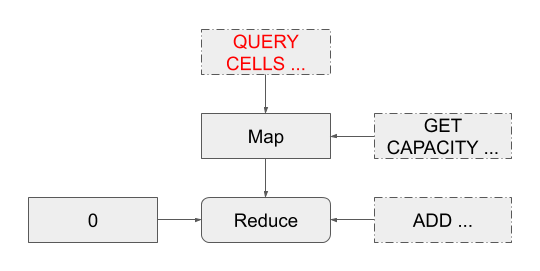
$ cd $TOP
$ cat << EOF > animagus/ruby/execution.rb
require_relative "ast_pb"
def build_execution_node(query_cell_node)
get_capacity_function = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::GET_CAPACITY,
children: [
Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::ARG,
u: 0
)
]
)
capacities = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::MAP,
children: [
get_capacity_function,
query_cell_node
]
)
add_balance_function = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::ADD,
children: [
Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::ARG,
u: 0
),
Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::ARG,
u: 1
)
]
)
initial_balance = Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::UINT64,
u: 0
)
Ast::Value::new(
t: Ast::Value::Type::REDUCE,
children: [
add_balance_function,
initial_balance,
capacities
]
)
end
def build_root(name, node)
Ast::Root::new(
calls: [
Ast::Call::new(
name: name,
result: node
)
]
)
end
EOF
现在我们准备构建 Animagus 所需的 AST 文件:
$ cd $TOP
$ pry -I animagus/ruby
[1] pry(main)> require 'query_cell'
[2] pry(main)> require 'execution'
[3] pry(main)> query_cell_node = build_query_cell
[4] pry(main)> execution_node = build_execution_node(query_cell_node)
[5] pry(main)> root = build_root("balance", execution_node)
[6] pry(main)> File.write("balance.bin", Ast::Root.encode(root))
正如上一篇文章中所说,我们可以用其他语言构建 AST,比如 Go,它也可以用来构建 Animagus。我们可以将所有内容都写在一个文件中,而不是将其扩展为两个文件和一个 REPL 部分。之所以选择这种方法,是因为 Ruby 提供了一个允许快速测试的 REPL。
如果你想要汇总一些其他节点的余额,可直接修改现有的 AST;如果只是想计算 cell 的数量而不是余额汇总,也可以修改 AST。学习 Animagus 的 AST 设计,其最好方法就是实际使用 AST。因此你可以随意修改我们在这里构建的 AST,也许你会发现 Ruby REPL 非常有用。
下面,我们在另一个终端窗口启动 Animagus(稍后我们将会用到 Ruby 来执行调用 Animagus,所以这里的 Ruby REPL 保持打开状态):
$ cd $TOP
$ ./animagus/animagus -astFile=balance.bin -graphqlUrl=http://127.0.0.1:9115/graphql
2020/03/04 03:41:34 Indexed block 92b197aa1fba0f63633922c61c92375c9c074a93e85963554f5499fe1450d0e5, block number 0
2020/03/04 03:41:34 Indexed block 2567f226c73b04a6cb3ef04b3bb10ab99f37850794cd9569be7de00bac4db875, block number 1
2020/03/04 03:41:34 Indexed block 2af0fc6ec802df6d1da3db2bfdd59159d210645092a3df82125d20b523e0ea83, block number 2
2020/03/04 03:41:34 Indexed block 247167d03a723f6b8999da09d94b61fadf47f94364d729cb6272edc1f20009b7, block number 3
2020/03/04 03:41:34 Indexed block 83832d6367429901a4bf763a6d6cbdc658a2624a8a4cda7427edd6fad65d0f7d, block number 4
2020/03/04 03:41:34 Indexed block 67a0604ef3147f82f81c44d8b74f7329ac4ebabc29a2931a88d64c8f44b77735, block number 5
(logs omitted..)
你会看到 Animagus 已经开始索引 CKB 的区块。也就是说即使 Animagus 还在索引,但它已经可以使用当前已索引的数据为 GRPC 提供请求了。这里需要注意,在 Animagus 还没赶上 CKB 的最新区块之前,数据可能并不准确。(因为后边索引的区块可能包含其他存取款信息)
为了达到测试的目的,现在我们运行实际的请求。但在生产环境中,可能需要等到 Animagus 赶上当时链的最新区块再运行。
现在我们回到之前的 Ruby REPL:
[12] pry(main)> require 'generic_pb'
[13] pry(main)> require 'generic_services_pb'
[14] pry(main)> stub = Generic::GenericService::Stub.new("127.0.0.1:4000", :this_channel_is_insecure)
[15] pry(main)> param = Ast::Value::new(t: Ast::Value::Type::BYTES, raw: ["903a0633f6ab457de09efb8f84dc271dc488bf62"].pack("H*"))
[16] pry(main)> request = Generic::GenericParams.new(name: "balance", params: [param])
[17] pry(main)> stub.call(request)
=> <Ast::Value: t: :UINT64, b: false, u: 89732200000000, raw: "", children: []>
在上面的示例中,我选择了 CKB 主网上的这个地址。我并不知道这是谁的地址,这只是一个创世块中尚未被使用的地址。用这样的一个地址,Animagus 能够快速而且不会有太多延迟地索引它的值。从实际的 GRPC 调用中,我们已经填写了 0x903a0633f6ab457de09efb8f84dc271dc488bf62 ,这是地址的 args 部分,在 balance checker AST 的参数 0 中使用。可以看到,我们已经获取了结果,即 89732200000000 shannons 或 897322 CKB。你可以随意将参数交换到另一个地址的 script args 进行尝试。
现在,我们已经使用 Animagus 实现了一个完整的地址余额查询。此示例比较简单,但你可以将其应用于构建更为复杂的示例,例如从多个地址汇总余额或 NervosDAO 的存款数。
只要你可以为 Animagus 提供一个用于提取和转换数据的 AST,Animagus 就可以转换成任何你想要的东西 。到这里,我想你会赞同 Animagus 这个名字非常适合这个项目。
以上就是有关如何运行 Animagus 的内容了,接下来,我们将研究如何使用 Animagus 集成 Simple UDT 规范。我们不仅会研究如何汇总 UDT 余额,还将展示如何使用 Animagus 将 UDT 从一个帐户转移到另一个帐户。
敬请期待!