#proof of work 2018 By Nervos CKB Team
By the end of 2017, there was a feeling that some ideas, including thoughts pertaining to a layered network protocol and the concept of a public blockchain as Common Knowledge Base, had come to a much mature state. Eager to roll into action, the group of us gathered in a small office soon after New Year’s Day of 2018 to have our very first discussion of CKB in a series to come, and worked out our first development plan. On January 23rd, the first line of code was written.
More than 300 days and nights has passed since. With many iterations and sprints, CKB has finally made it to version 0.1.0. To date, the system’s framework design has basically been completed with modules such as consensus, Cell Model, CKB-VM (CKB Virtual Machine) and P2P network protocol implemented and ready to become open-source. At last, the day has come to say: Hello CKB~
CKB Repositories
Nervos Network is a decentralized application network with a layered architecture. CKB (Common Knowledge Base) is a public blockchain protocol with a radically different design, is the foundational layer of Nervos Network, and it is designed to serve as the trust engine of the future crypto economy . Aligned with the Nervos’s goal of building a layered architecture, CKB aims to be the layer that stores assets and provides arbitration for all the upper-level layers.
Here are the GitHub repositories of CKB and CKB-VM (a RISC-V instructionset based virtual machine for verification scripts execution on CKB):
The programming model of CKB is comprised of the Cell Model and CKB-VM. All the DApps running on CKB will separate functionally into two parts: computation and verification (i.e. generation and validation as in CKB whitepaper). The verification is conducted on CKB, and executed by CKB-VM, while all computation should be processed off-chain. As this is a relatively new programming model, we provide some demos and an SDK as examples:
- https://github.com/nervosnetwork/mruby-contracts
- https://github.com/nervosnetwork/ckb-demo-ruby-sdk
- https://github.com/nervosnetwork/ckb-contract-debugger
It should be noted that: as CKB is still under rapid development, the API, programming model and some other designs may change in the future. Hence the simple example provided here is for reference purposes only.
As an open network, Nervos defines network standards and makes improvements upon the protocol through a process called RFC (Request for Comments). With this process, we invite community members to push development of Nervos Network forward. Here is the repository of Nervos RFCs :
CKB Features
- Adopts Rust as the primary programming language.
- Implements a concise and complete blockchain system by integrating different function modules.
- Adopts Cell Model (an extension of UTXO model) to support generic state storage.
- Uses Cell Model and CKB-VM based smart contract to separate computation and verification, with verification on-chain and computation off-chain.
- Supports decoupling of state and code in smart contract implementation.
- Enables smart contract programming with high-level programming languages such as Ruby and Python via CKB-VM which is based on RISC-V instruction set.
- Utilizes Flatbuffer as data serialization mechanism, which enables direct access to serialized data without parsing and achieves highly efficient memory usage based on zero-copy.
- Adopts a message-and-channel based mechanism for the system’s internal communication; the bottom-level storage access and index access are implemented using shared memory locking.
- Implements a secured P2P network with better resistance to attacks such as DoS and Eclipse attack.
- Adopts a highly efficient peer discovery and synchronization protocol.
CKB Main Components
SRC Module
SRC Module has the main function, and is the entry module for building the entire project.
Core Module
Core Module is for storing the definition of CKB’s core data structure, including Block, Transaction, Cell.
Spec Module
Spec Module is the configuration for the consensus module. This configuration will be written into the genesis block. Nodes that have different configurations cannot communicate with each other directly.
Shared Module
Shared module is for storing the shared code and logics between each of the modules.
DB Module
DB module encapsulates the data persistence layer. CKB utilizes Key-Value structure for data storage, which has two kinds of implementations: one is based on RocksDB and another one is based on memory simulation, which is mainly used for test and development scenarios.
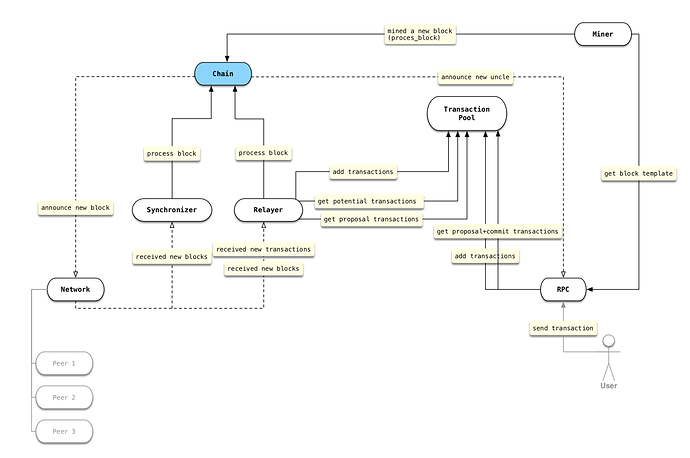
Chain Module
Chain module implements the blockchain data structure and uses DB module for data persistency. Chain module is responsible for updating the record of the local chain that has the most accumulated proofs of work. It also maintains the data index on blockchain. When updating the chain data, Chain module verifies the block and updates the data index.
Pool Module
Pool module mainly implements the transaction pool. One of CKB’s features is to adjust the block interval dynamically according to the network status, which could result in a more efficient network bandwidth utilization. The major challenge for designing and implementing the transaction pool for CKB is to reach a balance between multiple targets, including transaction ordering, dependencies and the overall performance level, especially reducing the data volume that needs to be synchronized between nodes and have a better utilization on the cache.
Protocol Module
Protocol module stores the definition of messages between nodes, as well as the builder of the message body. Messages use Flatbufferers for serialization.
Network Module
Network module implements the peer to peer communication mechanism. It encapsulates the rust-libp2p library and exposes some basic protocol in the form of services. By abstracting the rust-libp2p , it will be much more convenient to customize a new version of libp2p in the future.
Sync Module
Sync module implements the network synchronization protocol. It contains two protocols: one is the Synchronizer and the other one is the Relayer protocol. The Synchronizer protocol works in a head-first style, which makes efficient use of network bandwidth to improve block download efficiency and is used to download block data between nodes at high speed. The Relayer protocol is used between nodes to handle broadcasts and forward new transactions. Based on Bitcoin’s Head-first synchronization, Compact Block protocol, the Sync module integrates functions such as the transaction submission area and uncle block statistics.
CKB-VM Module
CKB-VM is an independent implementation of the RISC-V hardware CPU instruction set, and all implementations are fully compliant with RISC-V standards. So it can be considered as a General Sandbox Runtime Module. The role of CKB-VM in the project is to verify states and execute smart contracts, thereby providing flexibility to the computing layer of the entire system, such as adding new cryptographic algorithms by updating the smart contract stored in the system Cells. In addition, the isolated Sandbox design of CKB-VM provides strong security supports for executing contracts.
Miner Module
Miner module implements a pluggable mechanism for switching between different consensus algorithms. For development convenience, we have implemented two sets of built-in protocols: CPU and Cuckoo. It is also very easy to add an external consensus algorithm, such as ProgPoW algorithm.
Notify Module
Notify Module is a set of pub/sub modules for message communication between internal modules.
Explorer Module
Explorer module is a simple internal blockchain explorer for easily monitoring block data during development.
Devtools Module
Devtools module contains scripts implemented in Ruby for convenient delivery of test data to the blockchain during development.
Tips for Reading Codes
A certain level of background knowledge is required for reading code of Nervos CKB. Some pre-requisites may include the knowledge of Rust language and its development ecosystem, as well as some basic knowledge of data structure and algorithm. Basic concepts of blockchain, such as consensus protocols and smart contract will prove to be helpful as well.
Here’s three recommended paths for reading code:
- Data synchronization — this part of logic is most relevant to the network protocol and its implementation. Protocol module, Network module and Sync module are recommended to read.
- Data Storage — this part can help to understand the data structure design and the data persistency implementation. Core module, DB module, Chain Module and Pool module are recommended to read.
- Consensus Protocol — this part would require one to have a relatively deep understanding to the consensus algorithm. Spec module, PoW module, Sync Module and Chain module are recommended to read.
Nervos CKB is still in a phase of active development and its codes are yet to be battle-tested in a production level environment. It is likely that significant adjustments will be made to the existing functions and modules mentioned above. Please refer our GitHub repos for the most up-to-date information. Stay tuned!