Introduction
Since every transaction on the chain is transparent, and they could be linked and traced by the records. It actually undermines the fungibility of crypto-currency. And there have already been lots of companies exploiting the value of transaction traces. Chainalysis is one of the giant companies in this field.
The concept of coin join or mixer was firstly raised by Gregory Maxwell at 2012. Since then, tremendous works have been done to mitigate the concerns. The basic idea of coin join is to blend multiple users’ inputs and generate a multiple outputs, it is hard to link specific output with input from the perspective of an external observer.
A simple and trivial method to achieve coin join is to introduce some centralized mixer. The mixer collects users’ transfer intentions, combined them to a huge transaction, then return the transaction to the users to request signatures. Then the mixer broadcast the transaction, and everyone gets their transaction well processed in an unlinkable way. Obviously, this method exposes users’ privacy to the centralized mixer. But it’s easy to use and lots of such services are live until now.
There are two cryptography based decentralized mixer mechanisms in general, SNARKS and Ring-signatures. SNARKS based mixers are difficult to implement, require trust setup, heavy computation works to generate proof. Ring-signatures based mixers are good at fast computation, but not so good at proof size.
Another important thing we have to mention is the provider of the transaction fee or the sender of the transaction. Most of the chains require some sender to sign a transaction to claim tokens or execute smart contracts, and they also require someone to pay the transaction fee. Both of which will expose users’ privacy. To alleviate this concern, some projects introduce an agency role, like Tornado.cash, They actually shift the problem to another risk bottleneck, what if the agency is a Honeypot?
In this post, we propose a Ring-signature based mixer on CKB. It has the following advantages:
- Fully decentralized and non-custody, no trust setup, no agency
- Optimized performance, less than 1 seconds to generate the proof
- Great user experience, deposit anytime, withdraw anytime
- User defined privacy level, wait as long as you wish to gain better privacy
- Use brand-new addresses to withdraw, no likable transaction fee payer and transaction signer
- Works both for the native token and user defined tokens
Brief thought
Setup
There are several mix sets on-chain, according to different tokens and different amounts. Like 100, 1k, 10k for CKB, 1, 10, 1k, 10k for USDT, and so on. Every set contains a batch of depositors with the same amount of deposit.
Deposit
One deposits specific amount of token to the set cell, with a withdrawal address PK. Note that the PK must be a new one to preserve privacy. And the depositors need to deposit an extra amount of native token to pay the transaction fee in advance, deposit 1001 CK Bytes to the 1000 deposit set for example.
Withdrawal
After a random time and a random number of following depositors, you can withdraw your tokens. The users need to generate a proof by selecting a subset of PKs recorded in the deposit cell, and sign a ring signature to hide their identity, leave a key image to prevent the double-spending problem. With the proof and the transaction fee prepaid by the depositor, you can withdraw to a new address to perfectly hide your trails.
Draft specification
Schema
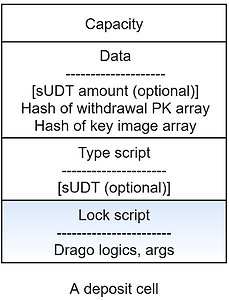
We use a deposit cell along with a specific lock script to handle the life cycle of the coin mixer. The data field of the deposit cell serves as the depositor registry, where records the hash of the withdrawal address PKs array and the hash of the key image array. Data availability is well secured when using hash instead of the original data array, because all the history records are in the previous block data, and we use witness to provide full data during on-chain verification. Meanwhile, we successfully get rid of the data accumulation problem in storing history PKs and key images on-chain.
The type script of the deposit cell is optional. You can create a deposit cell with UDT type script, then it accepts specific UDT only.
Create a deposit cell
Anyone could create a new Drago deposit cell with a specific token type and amount. It’s recommended that you’d better use an existing deposit cell to do the coin mix job, because it might have been accumulated lots of inputs and output, you can get better privacy. But for some circumstance, especially at the beginning, people need to create new deposit cells.
Initial parameters are necessary for the new deposit cells, including the token type (CKBytes or specific sUDT), token amount and prepaid transaction fees. All the parameters are encoded as args into the lock script.
Deposit assets
The deposit cell creator should be the first depositor, and they should complete the deposit along with the action of creation.
To deposit, one needs to provide exactly the same amount of tokens and exactly the same amount of prepaid transaction fees in CKBytes defined by the deposit cell. Besides, the depositor has to provide a withdrawal PK as an invoice for the future operation in witness. The withdrawal PK must be a brand new one, without being tainted before. It will be used to update the hash of the withdrawal PK array in the data field automatically.
Anonamous withdrawal
The receiver uses the secret key corresponding to previous committed PK in the deposit stage to claim their tokens. They have to provide the following data in the witness field of a withdrawal transaction.
- Full set of previous committed PK array
- Selected PK subset to make the ring signature group (with a bitmap data structure)
- Full set of previous withdrawal key image array
- Ring signature and corresponding key image
And the withdrawal transaction needs to update the following variables in the data field of the deposit cell.
- Hash of PK array
- Hash of key image array
- Token amount
Last withdrawal
Although the withdrawal process is anonymous, it is easy to find out whether a withdrawal order is the last one by counting the rest amount in the deposit cell.
It takes almost the same operations as an ordinary withdrawal, the only difference appears in the data update process. It will clear the PK array and the key image array to reduce the burden of witness data size.
Q&A
Why you name the coin mixer “Drago”?
There is a Chinese idiom reads literally: “one can see the head of a heavenly dragon, but not the tail”. Which is used to describe the mysterious things. So we hide the tail letter of the word “Dragon” to fit the idiom. LOL
What’s the specialty of Drago compared to other coinjoin solution on other chains?
Benefit from the user defined crypto primitives of Nervos CKB, Drago could achieve a real decentralized anonymous service on-chain. Any other platforms with fixed crypto primitives have to face the “transaction sender” problem. You have to use a transparent transaction sender to sign a TX and pay the TX fee to claim an anonymous token. Or you have to rely on an agency to send the TX instead of you, which expose your privacy to the agency.
References
[1] https://github.com/Mikerah/awesome-privacy-on-blockchains
[2] https://github.com/tvanepps/State-of-the-Mixers-Summer-2019
[3] Introducing Heiswap - An Ethereum Mixer
[4] Tornado Cash
[5] https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/CoinJoin